Risks and Challenges of Split Tunneling
VPN Split tunneling is a feature that allows users to divide their internet traffic into two distinct paths. While split tunneling offers numerous benefits, it also comes with certain risks and challenges that need to be considered. In this article, we will explore the risks associated with split tunneling and discuss the challenges that organizations may face when implementing this feature.
1. Increased Attack Surface
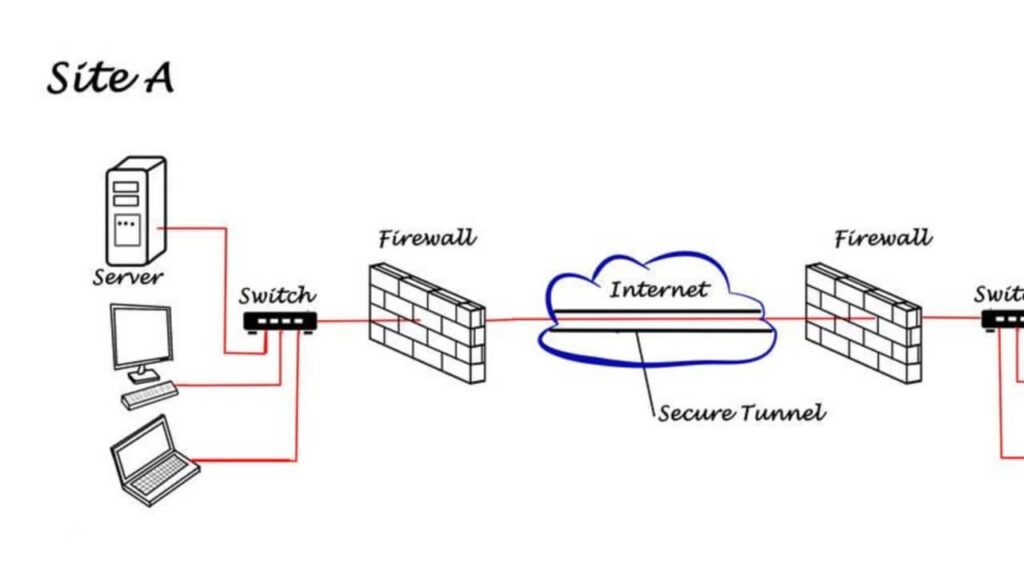
One of the main risks of split tunneling is the potential increase in the attack surface. When users direct certain traffic outside of the VPN tunnel, it bypasses the security measures provided by the VPN.

This can leave the non-VPN traffic vulnerable to various cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches. It is crucial for organizations to carefully assess the security implications of split tunneling and implement additional measures to mitigate these risks.
2. Data Leakage

Split tunneling introduces the risk of data leakage. If sensitive data is transmitted through the non-VPN tunnel, it can be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals. This is particularly concerning when employees connect to public or insecure networks, such as coffee shop Wi-Fi, where the risk of data interception is higher. Organizations must educate their employees about the risks associated with split tunneling and enforce strict security policies to prevent data leakage.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements

Certain industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict compliance and regulatory requirements regarding data security and privacy. Split tunneling may pose challenges in meeting these requirements as it involves routing sensitive data outside of the secure VPN tunnel.
Organizations operating in regulated industries must carefully evaluate the impact of split tunneling on compliance and ensure that appropriate measures are in place to maintain data integrity and confidentiality.
4. Network Performance and Bandwidth Management
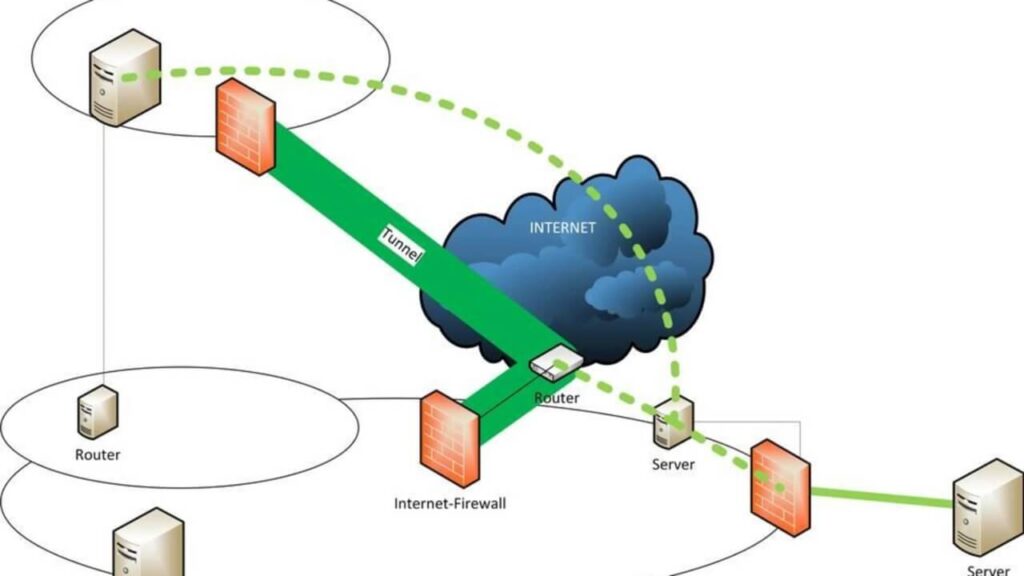
While split tunneling can enhance network performance by allowing non-sensitive traffic to bypass the VPN, it can also pose challenges in terms of bandwidth management.
If a large number of users direct bandwidth-intensive activities, such as streaming or downloading large files, outside of the VPN tunnel, it can impact the overall network performance and lead to congestion. Organizations need to implement effective bandwidth management strategies to ensure optimal network performance while maintaining security.
Best Practices for Implementing Split Tunneling
Implementing split tunneling requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. To mitigate the risks and challenges associated with split tunneling, organizations should follow these best practices:
1. Define Clear Security Policies

Establish clear security policies that outline which types of traffic should be routed through the VPN tunnel and which ones can bypass it. These policies should be based on the sensitivity of the data and the security requirements of the organization. Regularly communicate and enforce these policies to ensure consistent adherence.
2. Conduct Risk Assessments
Perform thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and risks associated with split tunneling. Assess the impact of split tunneling on data security, compliance requirements, and network performance. Use the findings of the risk assessments to develop appropriate mitigation strategies and controls.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication

To enhance the security of split tunneling, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for VPN access. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device. This helps prevent unauthorized access to the VPN and reduces the risk of data breaches.
4. Encrypt Non-VPN Traffic

Even though non-VPN traffic bypasses the VPN tunnel, it is still important to encrypt this traffic to protect it from interception.
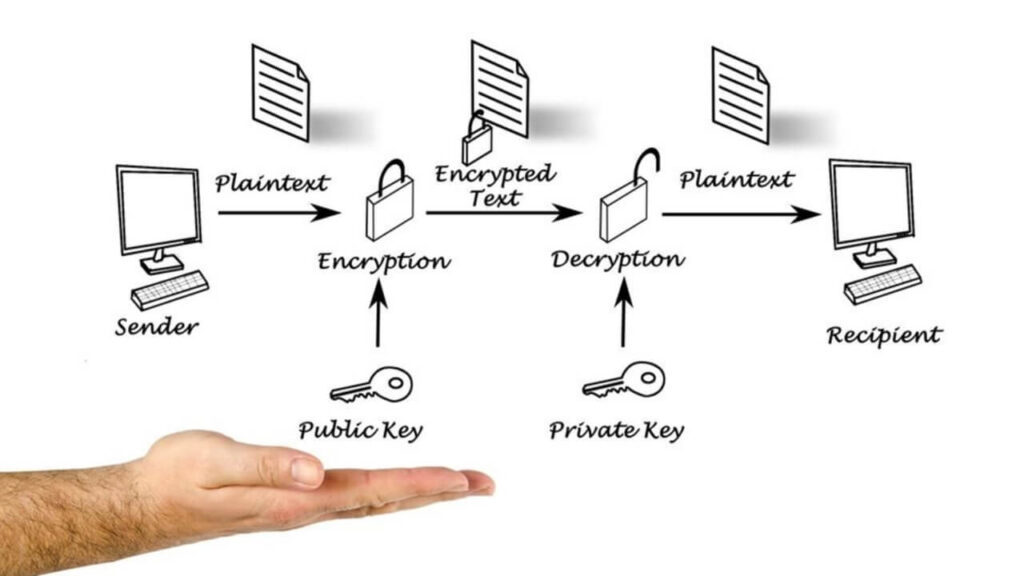
Implement encryption protocols, such as HTTPS, for non-VPN traffic to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data transmitted outside of the VPN tunnel.
5. User Education and Awareness

Educate employees about the risks and challenges of split tunneling. Train them on how to identify and avoid potential security threats when accessing the internet outside of the VPN tunnel. Promote awareness of best practices for secure internet browsing and emphasize the importance of adhering to the organization’s security policies.
In conclusion, while split tunneling offers benefits such as improved network performance and flexibility, it also introduces risks and challenges that organizations must address. By understanding and mitigating these risks through the implementation of best practices, organizations can leverage the advantages of split tunneling while maintaining the security and integrity of their data and network infrastructure.
























I am glad to be a visitor of this arrant weblog! , thankyou for this rare info ! .
You made various nice points there. I did a search on the subject and found mainly persons will go along with with your blog.
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say excellent blog!
I’ve read some good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a great informative web site.
Heya are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you need any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
Great post. I am facing a couple of these problems.
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove people from that service? Cheers!
Well I really liked reading it. This post provided by you is very constructive for proper planning.
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you¦ve on this site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What a great web site.
I am happy that I found this web blog, exactly the right information that I was looking for! .
It is perfect time to make some plans for the longer term and it’s time to be happy. I’ve learn this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some fascinating issues or tips. Perhaps you can write next articles regarding this article. I want to read more things about it!
This is the precise blog for anyone who desires to search out out about this topic. You understand so much its almost exhausting to argue with you (not that I really would need…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, just great!
Thanks for every other wonderful article. Where else may anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect manner of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I’m on the search for such info.
I’m not sure why but this blog is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thanks , I¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?