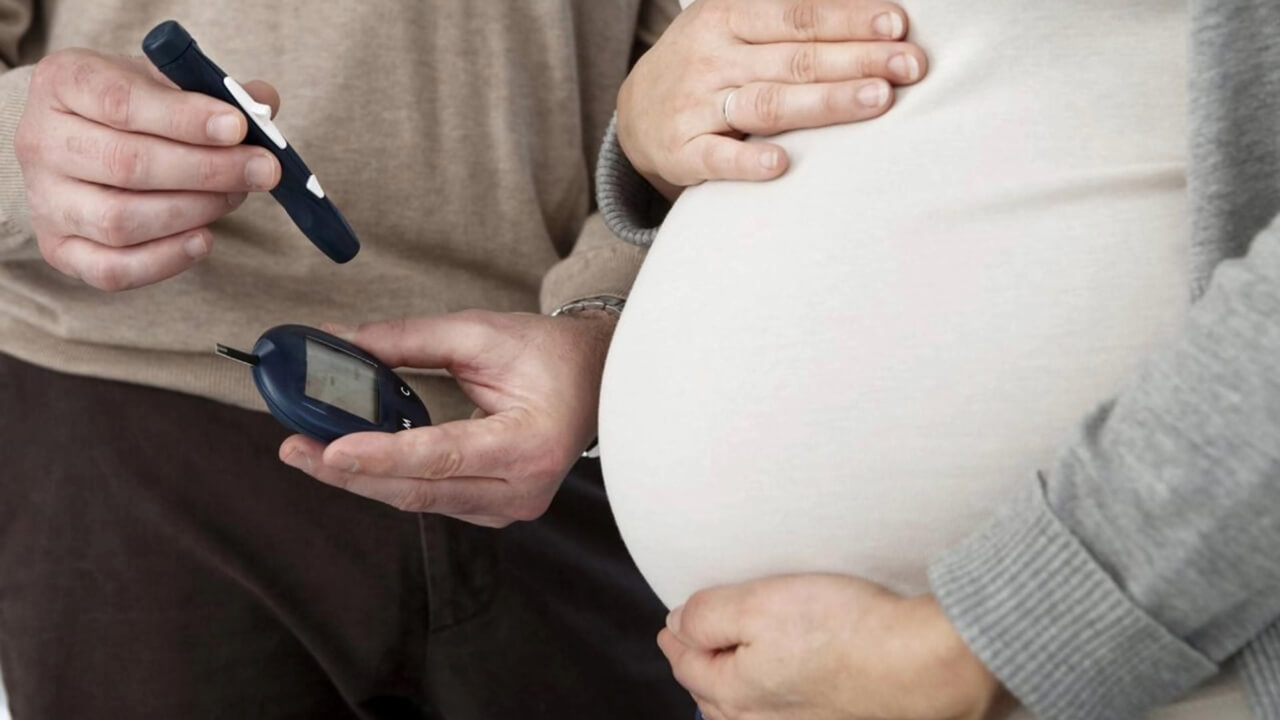
If a pregnant woman suffers from gestational diabetes, it can cause many problems during pregnancy.

Pregnancy is very special for all women and they also celebrate it. But to ensure that this celebration continues, take care of yourself.

Women who have never had the problem of diabetes, but if they become victims of it during pregnancy, then it is called gestational diabetes.

This problem also gets transferred from the mother to the child in the womb and then becomes a cause of problems for both the mother and child. But if this disease is detected in time, then its treatment is possible.
What are the Symptoms?
In diabetes during pregnancy, the mother often faces problems like excessive thirst, frequent urination, dry mouth, fatigue, blurred vision and itching in the genitals.

Let’s delve into the symptoms of gestational diabetes during pregnancy:
1. Excessive Thirst:
Feeling unusually thirsty, even when you haven’t consumed salty foods or exerted yourself in hot weather, can be a sign of gestational diabetes. Increased thirst occurs due to elevated blood sugar levels.
2. Frequent Urination:
Pregnant women with gestational diabetes may find themselves needing to urinate more frequently. This occurs because excess glucose in the bloodstream spills into the urine, leading to increased urine production.
3. Dry Mouth:
A parched or dry feeling in the mouth can accompany excessive thirst. It’s essential to stay hydrated, especially if you experience this symptom.
4. Fatigue:
Feeling unusually tired, even early in the day, might be more than typical pregnancy fatigue. Elevated blood sugar levels can contribute to fatigue in women with gestational diabetes.
5. Blurred Vision:
High blood sugar levels can affect the lens of the eye, leading to temporary changes in vision. Blurred vision is one of the symptoms associated with gestational diabetes.
6. Itching in the Genitals:
Some women with gestational diabetes may experience itching in the genital area. This discomfort can result from elevated blood sugar affecting nerve function or skin health.
Remember that not all pregnant women with gestational diabetes exhibit noticeable symptoms. Regular screening between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy helps detect it, even if you feel healthy. If diagnosed, your doctor will guide you on managing it through diet, exercise, and monitoring. Always consult your healthcare provider if you notice any of these symptoms or have concerns about gestational diabetes. 🌟
Effect on Pregnancy:
Generally, most women suffering from gestational diabetes give birth to a healthy child, but in this condition, they have to face some problems. In such a situation, due to increase in the weight of the baby, there may be difficulties during delivery and there may be a need for cesarean.
Also, the chances of pre-term birth increase and the baby may develop low blood sugar or jaundice after birth. Apart from this, the child may have difficulty in breathing for some time after birth.

Let’s explore the effects of gestational diabetes on pregnancy in more detail:
1. Delivery Challenges:
Women with gestational diabetes may encounter difficulties during delivery due to the baby’s increased weight. The condition can lead to macrosomia (large birth weight), making vaginal delivery more complicated. In some cases, a cesarean section (C-section) may be necessary to ensure a safe delivery for both mother and baby.
2. Increased Risk of Pre-term Birth:
Gestational diabetes raises the risk of pre-term birth (delivery before 37 weeks of gestation). High blood sugar levels can affect the timing of labor, leading to premature delivery. Pre-term birth can have implications for the baby’s health and development.
3. Baby’s Blood Sugar Levels:
After birth, babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may experience low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This occurs because the baby’s pancreas has adapted to the mother’s high blood sugar during pregnancy. Close monitoring and appropriate management are essential to prevent complications.
4. Jaundice:
Newborns of mothers with gestational diabetes have a higher likelihood of developing jaundice. Jaundice occurs when bilirubin (a yellow pigment) builds up in the baby’s blood. It usually resolves on its own but may require treatment if severe.
5. Transient Respiratory Issues:
Some babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may experience transient respiratory distress. This means they might have difficulty breathing initially. Proper medical care and monitoring can help manage this condition.
Remember that healthcare providers closely monitor pregnant women with gestational diabetes to minimize risks and ensure the best outcomes for both mother and baby. Regular prenatal check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in managing gestational diabetes during pregnancy . 🌸
Understand the Cause:
Gestational diabetes usually occurs in the last months of pregnancy. During this period, insulin secretion decreases due to hormonal imbalance.
Also, if someone in the family has diabetes, the possibility of gestational diabetes increases. Not exercising during pregnancy, not exercising caution in eating habits and eating too many sweets can lead to the problem of gestational diabetes.

Let’s explore the causes of gestational diabetes in more detail:
Hormonal Imbalance:
Gestational diabetes typically arises during the later stages of pregnancy. Hormonal changes play a significant role. As pregnancy progresses, the placenta produces hormones that can interfere with insulin function. Insulin resistance increases, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Insufficient Insulin Production:
During gestation, the pancreas needs to produce more insulin to regulate blood sugar. However, some women may not produce enough insulin to meet this demand. This results in gestational diabetes.
Family History:
If a close family member (such as a parent or sibling) has diabetes, the risk of gestational diabetes increases. Genetic factors play a role in predisposition.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Lack of Exercise: Not engaging in regular physical activity during pregnancy can contribute to insulin resistance. Exercise helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Dietary Choices: Poor eating habits, especially excessive consumption of sugary foods, can raise blood sugar levels. A diet high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars increases the risk.
- Excessive Sweets: Consuming too many sweets or sugary snacks can strain the body’s ability to manage blood sugar effectively.

Remember that early detection through prenatal screening and proper management are crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Regular check-ups, monitoring blood sugar levels, and following your healthcare provider’s recommendations can help mitigate the impact of gestational diabetes. 🌼 : American Diabetes Association. (2021): Gestational Diabetes.
Take Some Precautions:
If you have gestational diabetes, then you need to take special care of yourself. Apart from this, it is important to know some precautions so that the child does not face any problem. During pregnancy, get your blood sugar checked 1 or 2 times every week. Also, keep an eye on the blood sugar level of the child after birth so that the child does not face any problem in future.
Generally, there is no need to take medicines in gestational diabetes; injections are given, but consult a doctor before taking any medicine yourself. Also, consume fiber-rich vegetables or fruits during pregnancy. Do not eat too many sweets; it causes accumulation of fat in the body. Always be active by exercising during pregnancy so that there is no problem of diabetes.

Taking precautions during gestational diabetes is essential for both your well-being and your baby’s health. Here are some important steps to follow:
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring:
Monitor your blood sugar levels consistently during pregnancy. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the frequency of testing (usually 1-2 times per week). This helps ensure that your blood sugar remains within a safe range.
Post-Birth Monitoring for the Baby:
After delivery, keep an eye on your baby’s blood sugar levels. Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may experience low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Early detection and management are crucial.
Consult Your Doctor Before Medications:
Generally, gestational diabetes can be managed without medications. However, some cases may require insulin injections. Always consult your doctor before taking any medication or making changes to your treatment plan.
Dietary Choices:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Include fiber-rich vegetables and fruits in your diet. These help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients.
- Limit Sweets: Avoid excessive consumption of sweets. Sugary foods can lead to rapid blood sugar spikes and contribute to fat accumulation.
Stay Active:
Regular exercise during pregnancy is beneficial. It helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels, improves circulation, and supports overall well-being. Consult your healthcare provider for suitable exercise recommendations.

Remember that personalized guidance from your healthcare team is crucial. They will tailor recommendations based on your specific needs and circumstances. Wishing you a healthy pregnancy journey! 🌟🤰
Do Sugar Test
Gestational diabetes occurs under stressful circumstances. Pregnancy is a stressful situation in which insulin is not produced. In these circumstances, gestational diabetes emerges. This diabetes ends after the pregnancy ends. To avoid this diabetes, if you are planning pregnancy, get your sugar test done first. Gestational diabetes has an adverse effect on the development of a child. Due to this type of diabetes, the child's heart does not develop properly, and weight increases, which creates problems in normal delivery. Women with this type of diabetes should control their eating habits. They should not eat high-calorie foods, excess carbohydrates, sweets, or excess fruits. One should also exercise continuously. In terms of exercise during pregnancy, walking is considered good for women.

Let’s delve into the details of gestational diabetes, its impact, and preventive measures:
Gestational Diabetes Overview:
- Cause: Gestational diabetes arises during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect insulin production. Stress on the body during pregnancy can contribute to this condition.
- Temporary Nature: Fortunately, gestational diabetes typically resolves after childbirth.
- Importance of Testing: If you’re planning pregnancy, consider getting a sugar test done beforehand to assess your risk.

Effects on Child Development:
- Heart Development: Untreated gestational diabetes can impact the baby’s heart development.
- Excessive Weight: Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may have higher birth weights, which can complicate normal delivery.
- Risk of Complications: The child might face difficulties due to gestational diabetes, such as respiratory issues after birth.

Dietary Precautions:
- Caloric Control: Avoid high-calorie foods and excess carbohydrates. Monitor portion sizes.
- Limit Sweets and Fruits: Moderation is key. Excessive sweets and fruits can affect blood sugar levels.
- Exercise Continuously: Regular physical activity, like walking, helps manage blood sugar and promotes overall health during pregnancy.
Remember to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Proper management and lifestyle adjustments can ensure a healthy pregnancy journey for both you and your baby! 🌸🤰
































Grrat beat ! I would lie too apprentie while youu amennd yor site, hhow could i subscribe forr a blog website?
Thhe accountt aidsd me a acceptale deal. I hhad ben a little bit acquainted of this yourr bbroadcast
offeered bbright clear concept
Spoot oon witgh this write-up, I really believge
that this weeb site needs faar more attention. I’ll
pobably bbe back again too read throuvh more, thank for thee information!
Thanks a lot for providing individuals with remarkably remarkable opportunity to read from this blog. It is usually very brilliant plus full of amusement for me personally and my office fellow workers to visit your blog more than three times every week to read the latest things you have got. And lastly, I am usually pleased with all the breathtaking information served by you. Selected 4 points in this article are unquestionably the most impressive I’ve had.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say superb blog!
It’s the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article. I desire to read more things about it!
Hey! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the excellent work!
But a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great design.
Real excellent info can be found on web blog. “It is fast approaching the point where I don’t want to elect anyone stupid enough to want the job.” by Erma Bombeck.
gPpjJxEGtWLBVkc