Are you also troubled by acne and want a glowing skin, then listen to the experts only, not everyone.

Many women have acne problems, due to which their skin starts looking bad. This problem can affect a person of any age. When acne occurs, the pores of the skin get clogged and oil and dead skin cells accumulate in them, which causes pimples and other skin problems.
Everyone’s skin is different and the ways to take care of it are also different. Therefore, it is important for you to take some precautions to take care of acne prone skin.
Cleanser:
Cleanser is most important for deep cleaning of our skin and removing oil and dust particles, but using a cleanser different from the skin type can make the skin dry and acne can also increase. If you want, you can use a normal face wash, but do not wash your face repeatedly in the insistence of cleaning your face, this will make the skin more dry.

Let’s dive into the world of cleansers and explore their benefits and proper usage.
What Is a Cleanser?
A cleanser is a skincare product designed to remove makeup, dirt, excess oil, dead skin cells, and other impurities from the surface of your skin. It’s like your trusted sidekick in battling away the day’s grime. Here’s what cleansers do:
- Deep Cleaning: Cleansers actively remove buildup that can clog your pores and contribute to breakouts.
- Hydration: They not only prevent breakouts but also hydrate and refresh your skin.
Types of Cleansers:
Different cleansers cater to various skin types. Here are some common types:
- Gel Cleansers: Ideal for oily or acne-prone skin, as they tackle excess oil.
- Cream Cleansers: Rich in moisture, these soothe dry or sensitive skin.
- Foaming Cleansers: Light and suitable for normal to combination skin.
Remember, individual cleansers vary based on brand and ingredients. Look for specific ingredients that match your skin type. For instance:
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid provides hydration.
- Sensitive Skin: Chamomile soothes.
- Oily Skin: Salicylic acid can be helpful.
How to Use Cleanser Properly:
- Apply: Massage the cleanser into your skin, working it in gently.
- Rinse: Rinse with water and pat your skin dry.
- Pair with Moisturizer: Follow up with a replenishing moisturizer to keep your skin balanced.
Remember, quality matters more than quantity. Avoid overwashing your face, as excessive cleansing can lead to dryness. Choose a cleanser that suits your skin type, and enjoy the benefits of a fresh, clean canvas! 🌟
For personalized recommendations, consider trying the Colorescience Barrier Pro™ 1-Step Cleanser—it’s powerful yet gentle.
Say No to Scrub:
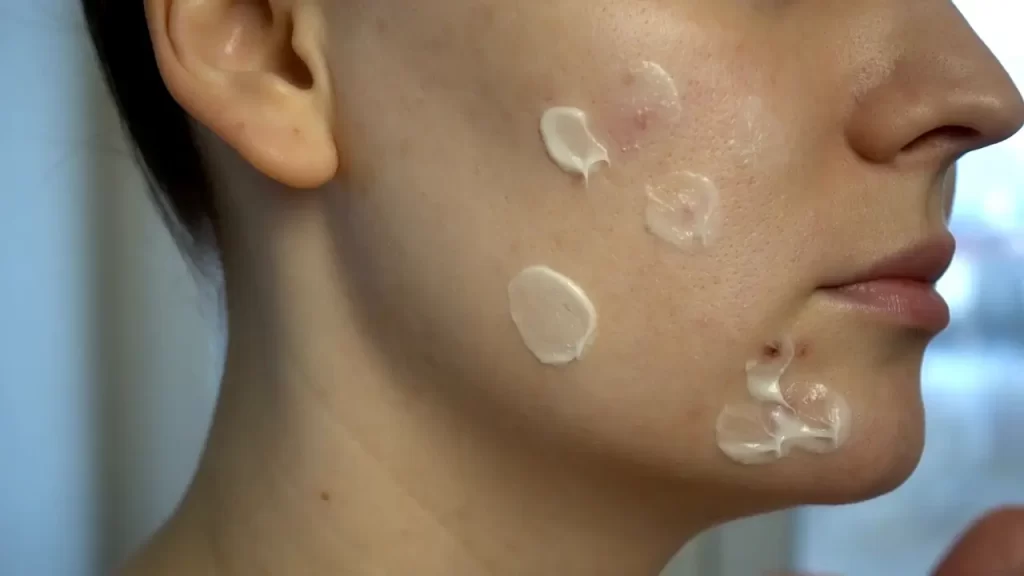
Scrub works to clean our skin and remove dead skin cells. You should never scrub and do face massage on acne prone skin, because these can cause acne to spread. Often people also use face packs to cure acne, but this increases acne even more.
Let’s delve into the world of skincare and explore why saying “no” to scrubbing might be beneficial for your skin, especially if you’re prone to acne.
The Purpose of Scrubs:
- Exfoliation: Scrubs, also known as exfoliants, are designed to physically remove dead skin cells from the surface of your skin. They use gentle abrasives (such as sugar, salt, or microbeads) to slough off the top layer, revealing fresher skin underneath.
- Smoothness: Regular exfoliation leaves your skin feeling smoother and more even.
Why Say No to Scrub?
1. Acne-Prone Skin: If you have acne-prone skin, aggressive scrubbing can exacerbate the issue. Here’s why:
- Spread of Acne: Scrubbing vigorously can irritate existing acne lesions and spread bacteria to nearby areas.
- Inflammation: Acne-prone skin is often inflamed. Rough scrubbing can worsen inflammation and redness.
- Microtears: Overzealous scrubbing can create tiny microtears in the skin, making it more susceptible to infection.
2. Face Massage: While facial massages can be relaxing, they should be gentle and mindful. For acne-prone skin:
- Avoid Vigorous Massages: Aggressive massages can disturb acne lesions and lead to more breakouts.
- Choose Light Pressure: Opt for light, circular motions to improve blood circulation without aggravating acne.
3. Face Packs: Some face packs claim to cure acne, but not all are suitable:
- Ingredients Matter: Look for face packs with non-comedogenic ingredients (those that won’t clog pores).
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Harsh chemicals can worsen acne. Natural ingredients like tea tree oil or aloe vera may be better choices.
What to Do Instead:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser suitable for your skin type. Avoid harsh soaps or aggressive scrubbing.
- Chemical Exfoliation: Consider chemical exfoliants (like salicylic acid or glycolic acid) instead of physical scrubs. They dissolve dead skin cells without abrasion.
- Moisturize: Hydrate your skin to maintain its protective barrier.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If acne persists, seek professional advice. They can recommend personalized solutions.
Remember, skincare is not one-size-fits-all. Listen to your skin, observe its reactions, and adjust your routine accordingly. 🌟
How to moisturize:

Sometimes our acne becomes dry and a scab starts forming on it, on which we apply moisturizer. But doing this is wrong. You should never apply oil based moisturizer on oily skin. These increase the amount of oil in our skin, due to which acne increases instead of reducing. If you want to keep your skin hydrated, then buy moisturizers with light formula, which have less amount of oil.
Let’s dive into the world of moisturizers and explore how to keep your skin hydrated without exacerbating acne, especially if you have oily skin.
Why Moisturize Oily Skin?
- Balancing Act: Even oily skin needs hydration. Skipping moisturizer can lead to overcompensation—your skin produces more oil to compensate for the lack of moisture.
- Preventing Dryness: Acne treatments can sometimes dry out the skin. Proper moisturizing helps maintain a healthy skin barrier.
Choosing the Right Moisturizer for Oily Skin:
- Lightweight Formulas: Opt for water-based or gel-based moisturizers. These won’t feel heavy or clog pores.
- Non-Comedogenic: Look for products labeled “non-comedogenic.” These won’t block your pores.
- Oil-Free: Choose oil-free or oil-absorbing moisturizers.
- Avoid Heavy Ingredients: Shea butter and other heavy emollients may be too much for oily skin.
Moisturizer Recommendations for Oily Skin:
- Neutrogena Hydro Boost Gel-Cream: Lightweight, hydrating, and oil-free. Contains hyaluronic acid and glycerin
- Peter Thomas Roth Water Drench Hyaluronic Cloud Cream: Anti-aging formula with hyaluronic acid. Hydrates without feeling heavy
- Origins Clear Improvement Moisturizer: Suitable for acne-prone skin
- Yes To Tomatoes Daily Balancing Moisturizer: Vegan formula for balancing oily skin
- Cetaphil DermaControl Oil Absorbing Moisturizer SPF 30: Great for oily, acne-prone skin
Remember, a well-chosen moisturizer can keep your skin hydrated without worsening acne. 🌟
Anti Acne Cream:

It is not wrong to use anti acne cream on acne prone skin, but consult a dermatologist before using any kind of anti acne cream. If you apply anything on your skin on someone’s advice, then you may also have its side effects.
Let’s delve into the world of anti-acne creams and understand how to use them effectively, especially if you have acne-prone skin.
Anti-Acne Creams: What You Need to Know
- Consult a Dermatologist: Before using any anti-acne cream, seek professional advice. A dermatologist can recommend the most suitable product based on your skin type and specific concerns.
- Individual Variability: Everyone’s skin reacts differently. What works for one person may not be ideal for another. Personalized guidance is crucial.
- Side Effects: Some anti-acne creams can cause side effects, such as dryness, redness, or irritation. A dermatologist can help you navigate these potential risks.
General Tips for Using Anti-Acne Creams:
- Patch Test: Always perform a patch test before applying any new product to your face. Apply a small amount to a small area (like behind your ear) and observe for any adverse reactions.
- Start Slowly: Introduce the cream gradually. Begin with a small amount and assess how your skin responds.
- Follow Instructions: Read the instructions provided with the cream carefully. Some creams are meant for spot treatment, while others can be used all over the face.
- Consistency: Consistent use is key. Don’t expect overnight results; give the product time to work.
- Sun Protection: Some anti-acne creams increase sun sensitivity. Use sunscreen during the day to protect your skin.
Remember, professional guidance ensures you make informed choices for your skin. 🌟
Home remedies:

We use home remedies for many skin related problems, but when it comes to acne prone skin, we should be a little careful. If you have a lot of acne problem, then you should avoid any kind of home remedy. If there is more itching or redness on the acne area, you can use coconut oil.
Let’s explore home remedies for acne-prone skin and understand how to approach them with care.
Home Remedies for Acne-Prone Skin:
Be Cautious: While home remedies can be effective, they’re not universally suitable. Consider the following:
- Severity: If you have severe acne, consult a dermatologist before trying any home remedy.
- Individual Reactions: Everyone’s skin reacts differently. What works for one person may not work for another.
Avoid Overdoing It:
Excessive experimentation with home remedies can worsen acne. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Gentle Approach: Opt for mild remedies. Harsh treatments can irritate your skin.
- Patch Test: Always do a patch test before applying anything to your face.
Coconut Oil:
While coconut oil is popular, it’s not universally recommended:
- Pros: It has antimicrobial properties and can soothe dry skin.
- Cons: Coconut oil is comedogenic (can clog pores). Use it sparingly and only if it suits your skin.
Other Home Remedies:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties. Dilute it and apply as a spot treatment.
- Honey: Has natural antibacterial properties. Apply a thin layer to affected areas.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes inflammation and redness. Use fresh aloe gel.
Remember, moderation and individualized care are key. If you experience excessive itching or redness, discontinue the remedy and seek professional advice. 🌟
For personalized recommendations, consider consulting a dermatologist who can guide you based on your specific skin needs.
Vitamin ‘C’ Should be in the Diet

Acne mostly occurs on oily skin and can also increase if disturbed too much. Therefore, acne prone skin needs special care. Nowadays, products are available in the market for every kind of problem related to the face, but using them without information can make your skin lifeless. Many times, using these beauty products can also cause you problems like allergy or skin irritation. Home remedies without knowledge can also harm your skin. Therefore, it is best to include foods rich in vitamin C in your diet, as it helps in maintaining pigmentation.
Let’s explore the role of vitamin C in skincare, especially for acne-prone skin.
Vitamin C and Acne: A Closer Look
- Antioxidant Power: Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, acts as a potent antioxidant. It helps protect your skin cells from free radical damage caused by factors like UV rays, pollution, and stress.
- Skin Healing: Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for skin structure and regeneration. Collagen helps wounds heal and maintains skin firmness.
- Reducing Inflammation: Acne is an inflammatory condition characterized by blocked pores, redness, and swelling. Vitamin C’s anti-inflammatory properties may help improve the appearance of acne lesions by reducing redness and swelling.
How to Incorporate Vitamin C:
1. Diet: Include foods rich in vitamin C:
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits)
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries)
- Kiwi
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
2. Supplements: Consult a healthcare professional before taking vitamin C supplements.
Remember, a balanced diet with vitamin C can contribute to healthy skin and overall well-being! 🌟




























I am impressed with this website , real I am a big fan .
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the internet the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people consider worries that they just don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
Terrific paintings! That is the type of information that are supposed to be shared across the net. Shame on Google for not positioning this put up higher! Come on over and consult with my site . Thanks =)
There is visibly a lot to identify about this. I suppose you made certain good points in features also.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation however I in finding this matter to be really something that I think I’d by no means understand. It sort of feels too complicated and very extensive for me. I am having a look ahead in your next submit, I’ll try to get the dangle of it!
I used to be very pleased to seek out this internet-site.I needed to thanks in your time for this excellent learn!! I definitely having fun with each little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
You made some first rate factors there. I regarded on the internet for the problem and located most individuals will go together with along with your website.
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
Great blog here! Additionally your site so much up fast! What web host are you the use of? Can I get your associate hyperlink to your host? I desire my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation however I to find this matter to be really one thing that I think I might by no means understand. It sort of feels too complicated and extremely large for me. I am taking a look ahead for your next publish, I’ll attempt to get the dangle of it!
I used to be recommended this website via my cousin. I’m now not positive whether this post is written by way of him as no one else recognize such special about my problem. You are wonderful! Thanks!
Its like you learn my mind! You appear to know so much approximately this, such as you wrote the e book in it or something. I think that you simply could do with a few p.c. to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is fantastic blog. A fantastic read. I will definitely be back.